Aresearch team at the National University of Singapore (NUS,Singapore;www.nus.edu.sg) has created an ingestible X-ray dosimeter capable of real-time radiation dose detection.
By integrating their innovative capsule design with a neural-network-based regression model that calculates radiation dose based on data captured by the capsule, the researchers achieved approximately five times more accurate dose monitoring compared to existing standard methods.
The novel ingestible X-ray dosimeter can measure radiation dose, pH changes, and temperature in real time during gastrointestinal radiotherapy.
While currently designed for monitoring radiotherapy doses in gastric cancer, the capsule could also be adapted to track treatment for various malignancies with modifications to its size.
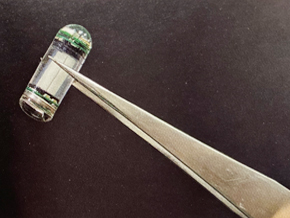
lmage: The components of the dosimeter can fit into an 18mm by 7mm capsule (Photo courtesy of University of NUS)
