Engineers at The University of New South Wales (UNSW,Sydney,and flexible robotic arm that could be utilized to 3D print biomaterial directly onto organs within the human body.
This soft robot can be inserted into the body in the same way as an endoscope and has the capacity to directly deliver multilayered biomaterials right onto the surface of internal organs and tissues.
The proof-of-concept device,known as F3DB, features a highly maneuverable swivel head that 'prints' the bioink, attached to the end of a long and flexible snake-like robotic arm,all of which can be controlled externally.
The printing head,which consists of soft artificial muscles that enable it to move in three directions, functions similarly to conventional desktop 3D printers.
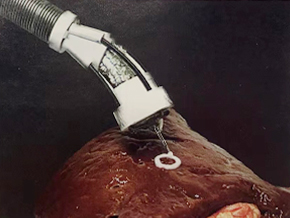
Image: A new soft robot makes 3D bioprinting inside the human body possible(Photo courtesy of UNSW)
